- Home
- Research Navigation
-
Products
- Recombinant antibody
- Tag Nano-Antibody
- Recombinant Tag Antibody
- Nano-Secondary Antibody
- Recombinant Secondary Antibody
- For IP Nano-Secondary Antibody
- For WB Nano-Secondary Antibody
- Nanoselector
- Smart Ligands®
- Smart Booster
- SmartCapture® For Purification
- Flow Cytometry Antibody
- Recombinant VHH
- Antibody Biosimilar
-
Service
- Technical support
- About
- Blog
CAR Molecular Development
CAR-T (Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell Therapy) immunotherapy uses CAR to identify tumor cells and release cytokines to exert anti-tumor effects. CAR is mainly composed of extracellular domains, transmembrane domains, and intracellular domains. The antibody fragment (scFv or VHH) in the extracellular domain can determine the specificity and affinity of the antigen, the transmembrane domain can affect the expression of CAR on the cell surface, and the co-stimulatory domain and signal transduction domain in the intracellular domain play a role in signal activation and transduction to enable T cells to exert their lethality. Among them, the antibody preparation process with good specificity and high affinity will help to screen CAR sequences with small side effects and strong lethality.
For CAR post-selection molecules, AlpVHHs has established three antibody development platforms (phage antibody library, hybridoma, yeast display, etc.), which can obtain diverse binding sequences to meet the needs of scFv and VHH discovery. Through the analysis of candidate molecules, multi-epitope or multi-specific CAR molecules can be prepared.
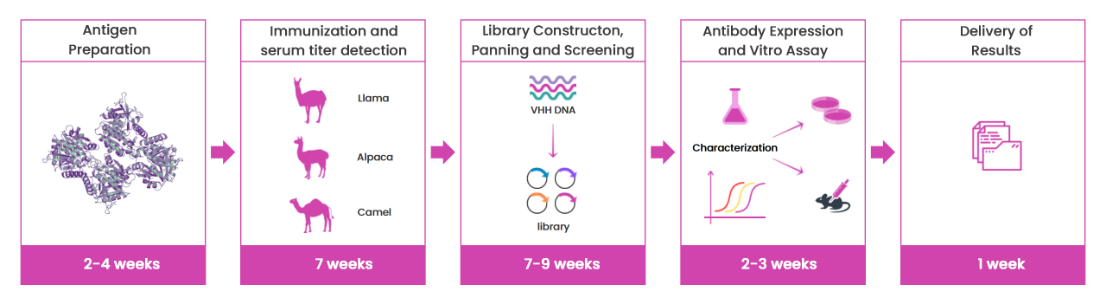
Service Process
Service Advantages

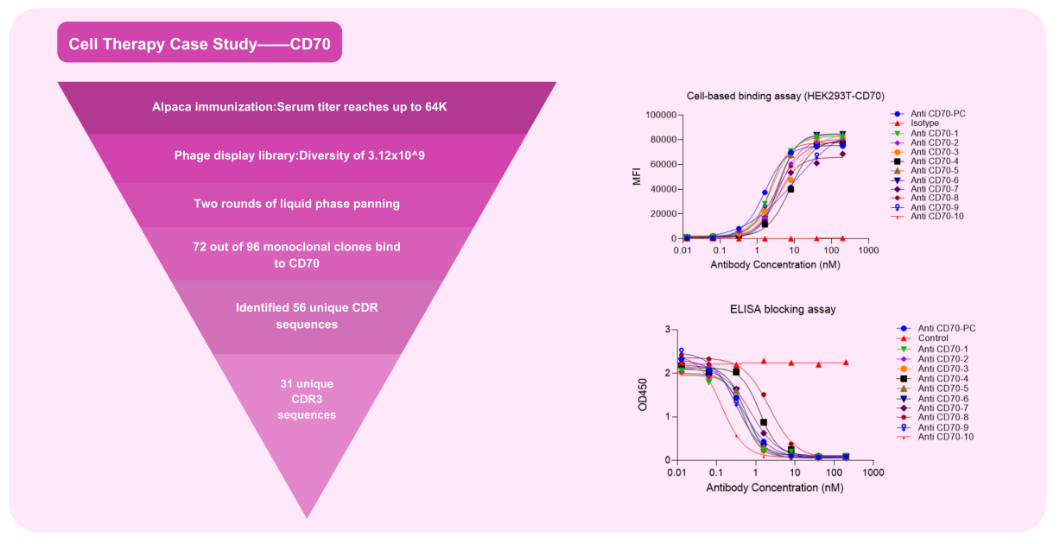
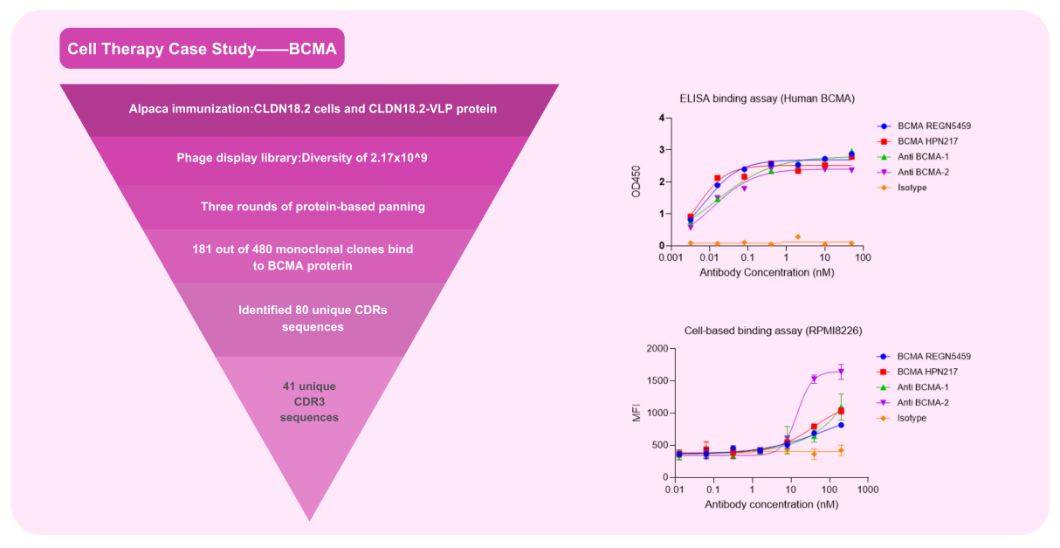
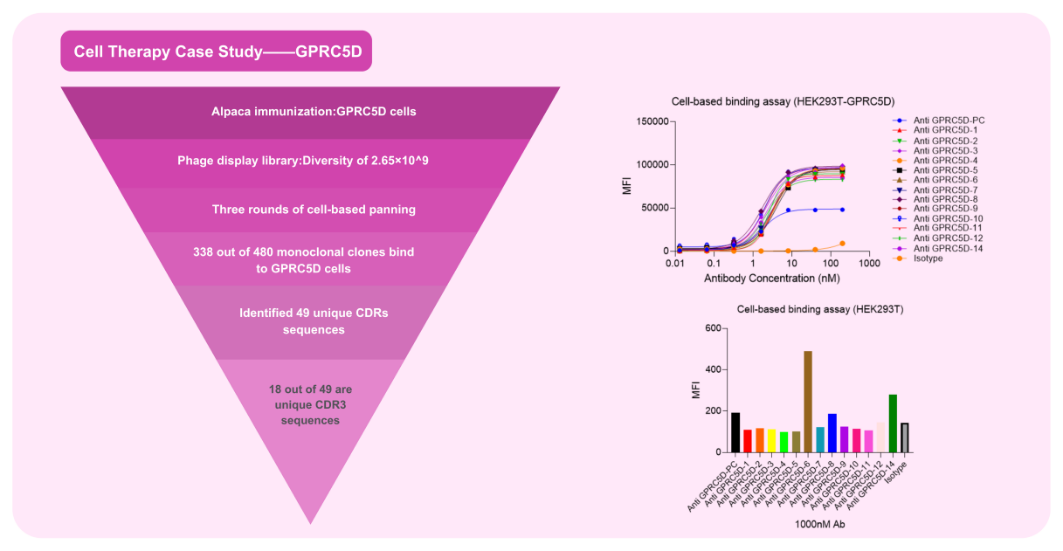
CAR Domain VHH Antibody Development Case Study